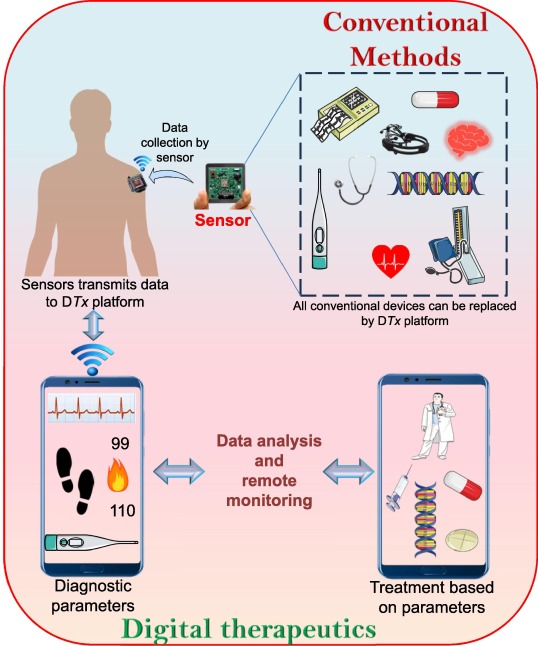
The Rise of Health Technology: An Overview
Health technology, often shortened to health tech, is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape. It encompasses a wide range of tools, devices, and software designed to improve patient care, streamline healthcare operations, and enhance overall health outcomes. From wearable fitness trackers to sophisticated diagnostic imaging systems, health tech is impacting every aspect of medicine.
This article delves into the key trends, challenges, and opportunities within the health tech sector. We’ll explore how these innovations are reshaping the future of healthcare delivery.
Key Areas of Innovation in Health Technology
Several key areas are driving innovation in health tech. Let’s examine some of the most impactful:
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations and monitoring are expanding access to care, especially in underserved areas.
- Wearable Devices: Fitness trackers and smartwatches are providing valuable data for personalized health management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used for everything from drug discovery to diagnostic imaging analysis.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital records are improving data sharing and coordination of care.
- Robotics: Surgical robots are enhancing precision and minimizing invasiveness.
Challenges and Opportunities in Health Tech Adoption
While health tech offers immense potential, several challenges must be addressed to ensure widespread adoption. These include:
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting sensitive patient data is paramount.
- Interoperability: Systems must be able to communicate with each other seamlessly.
- Cost and Reimbursement: The cost of new technologies can be a barrier to access. Clear reimbursement pathways are needed.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the regulatory landscape can be complex.
- Digital Literacy: Patients and providers need to be comfortable using new technologies.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities are vast. Health tech has the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and create a more efficient and equitable healthcare system.
The Future of Health Technology: What to Expect
The future of health tech is bright. We can expect to see even more sophisticated and personalized solutions emerge. Here are a few trends to watch:
Personalized Medicine
Genetic testing and other advanced technologies will enable more tailored treatments based on individual patient characteristics.
Predictive Analytics
AI and machine learning will be used to predict disease risk and identify patients who would benefit from early intervention.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR will be used for training, rehabilitation, and pain management.
Decentralized Clinical Trials
Technology will enable more patients to participate in clinical trials from the comfort of their own homes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Ethical Considerations in Health Technology Deployment
The rapid advancement of health technology necessitates a rigorous examination of the ethical implications inherent in its deployment. These considerations extend beyond mere regulatory compliance and delve into the fundamental principles of patient autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice. The integration of artificial intelligence, for instance, raises concerns regarding algorithmic bias and the potential for discriminatory outcomes. Furthermore, the collection and utilization of vast datasets require robust safeguards to protect patient privacy and prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
A proactive and ethical framework is paramount to ensure that health technology serves to enhance, rather than compromise, the well-being of individuals and communities. This framework should encompass:
- Transparency: Algorithms and decision-making processes should be transparent and explainable to both clinicians and patients.
- Accountability: Clear lines of responsibility should be established for the development, deployment, and monitoring of health technology.
- Fairness: Measures should be implemented to mitigate bias and ensure equitable access to the benefits of health technology.
- Data Security: Robust security protocols should be in place to protect patient data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Patient Consent: Informed consent should be obtained from patients regarding the collection and use of their data.
The ongoing dialogue between technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals is crucial to navigate these complex ethical challenges and ensure the responsible development and implementation of health technology.
The Role of Government and Regulatory Bodies
Government agencies and regulatory bodies play a critical role in shaping the health technology landscape. Their responsibilities include establishing standards for safety, efficacy, and interoperability; ensuring data privacy and security; and promoting innovation while safeguarding patient interests. The regulatory environment must be adaptable and responsive to the rapid pace of technological change, while also providing clear guidelines for manufacturers, developers, and healthcare providers.
Key areas of focus for government and regulatory bodies include:
- Establishing clear regulatory pathways for new health technologies: This includes defining the requirements for pre-market approval, clinical trials, and post-market surveillance.
- Promoting interoperability standards: Ensuring that different health technology systems can communicate with each other seamlessly is essential for effective data sharing and coordination of care.
- Enforcing data privacy and security regulations: Protecting patient data from unauthorized access and breaches is paramount.
- Addressing ethical concerns: Developing guidelines for the ethical use of artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies.
- Supporting research and development: Investing in research and development to accelerate the development of innovative health technologies.
Effective collaboration between government, industry, and academia is essential to create a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while protecting patient safety and promoting public health.
Investing in Health Technology: A Strategic Perspective
Investment in health technology is not merely a financial endeavor; it represents a strategic commitment to improving healthcare outcomes, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation. Investors, both public and private, are increasingly recognizing the transformative potential of health technology and are allocating significant capital to support its development and deployment. However, successful investment requires a thorough understanding of the market dynamics, regulatory landscape, and technological trends.
Key considerations for investors in health technology include:
- Market size and growth potential: Identifying areas of unmet need and assessing the potential market for new technologies.
- Competitive landscape: Evaluating the existing competition and identifying opportunities for differentiation.
- Regulatory environment: Understanding the regulatory requirements for bringing new technologies to market.
- Reimbursement landscape: Assessing the potential for reimbursement from payers.
- Team and technology: Evaluating the strength of the management team and the underlying technology.
A long-term perspective and a willingness to embrace risk are essential for successful investment in health technology. The potential rewards, however, are significant, both in terms of financial returns and the positive impact on human health.
css
/* Basic Styling for the Blocks /
.info-block {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
padding: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
position: relative; / For the colored stripe /
overflow: hidden; / To contain the shadow /
}
.info-block h2 {
margin-top: 0;
color: #333;
}
.info-block ul {
list-style-type: disc;
margin-left: 20px;
}
/ Colored Stripe /
.info-block::before {
content: “”;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
width: 5px;
background-color: #4CAF50; / Example color /
}
/ Callout Styling /
.callout {
background-color: #e9ecef;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 15px;
margin-top: 15px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
font-style: italic;
border-left: 5px solid #007bff; / Example color /
}
/ FAQ Section Styling /
.faq-section .faq-question {
font-weight: bold;
margin-top: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.faq-section .faq-answer {
padding: 10px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
border-radius: 5px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
display: none; / Initially hide the answers /
}
.faq-section .faq-question:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
/ Style for the title /
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
Explanation of CSS:
`.info-block`: This is the main container for each section. It sets the background color, rounded corners, shadow, padding, and margin. `position: relative` is crucial for positioning the colored stripe. `overflow: hidden` prevents the shadow from being clipped by the rounded corners.
- `.info-block::before`: This creates the colored stripe on the left. It’s a pseudo-element positioned absolutely within the `.info-block`.
- `.callout`: Styles the informational callouts with a different background color, padding, and a colored border on the left.
- `.faq-section`: Styles the FAQ section.
- `.faq-section .faq-question`: Styles the questions in the FAQ.
- `.faq-section .faq-answer`: Styles the answers in the FAQ and initially hides them using `display: none;`. You would need JavaScript to toggle the visibility of the answers when the questions are clicked.
- `h1`: Styles the main title of the article.
Important Considerations and Improvements:
- JavaScript for FAQ: The FAQ section currently hides the answers. You’ll need JavaScript to make the answers appear when the questions are clicked. A simple example:
javascript
document.querySelectorAll(‘.faq-question’).forEach(question => {
question.addEventListener(‘click’, => {
const answer = question.nextElementSibling;
answer.style.display = answer.style.display === ‘block’ ? ‘none’ : ‘block’;
});
});
- Responsiveness: The CSS provided is a basic starting point. You’ll need to add media queries to make the design responsive and adapt to different screen sizes (e.g., mobile phones, tablets).
- Accessibility: Ensure your design is accessible to users with disabilities. Use semantic HTML, provide alternative text for images, and ensure sufficient color contrast.
- Color Palette: Choose a consistent and visually appealing color palette. Consider using a color palette generator or consulting with a designer.
- Font Choices: Select fonts that are easy to read and appropriate for the tone of your article.
- Image Optimization: If you include images, optimize them for the web to reduce file size and improve loading speed.
- Testing: Thoroughly test your design on different browsers and devices to ensure it works correctly.
- More Advanced Styling: You can use more advanced CSS techniques like Flexbox or Grid for more complex layouts.