Forex trading, the world’s largest and most liquid financial market, offers incredible opportunities for profit. But let’s be honest, it’s not all sunshine and roses. The potential for significant gains comes hand-in-hand with the very real risk of substantial losses. Understanding and managing this risk is absolutely crucial for long-term success. So, how do you navigate this complex landscape and protect your capital? Let’s dive into the essential methods for calculating risk when trading forex.
Understanding Forex Risk Calculation
Before you even think about placing a trade, you need to grasp the fundamental concept of risk calculation. It’s not just about guessing; it’s about using specific tools and strategies to quantify your potential losses. Why is this so important? Because knowing your risk allows you to make informed decisions, control your emotions, and ultimately, stay in the game longer. Think of it like this: would you drive a car without knowing how to use the brakes?
Key Components of Forex Risk Calculation
- Position Size: The amount of currency you’re trading.
- Stop-Loss Order: A predetermined price level at which your trade will automatically close to limit losses.
- Leverage: Borrowed capital that magnifies both potential profits and losses.
- Pip Value: The value of a single “point in percentage” (pip) movement for a specific currency pair.
These elements work together to determine the overall risk associated with each trade. Ignoring even one of them can lead to unexpected and potentially devastating results.
Tip: Always determine your risk tolerance before you start trading. This will help you set appropriate stop-loss levels and manage your position sizes effectively.
Calculating Risk Using Pip Value and Stop-Loss Orders
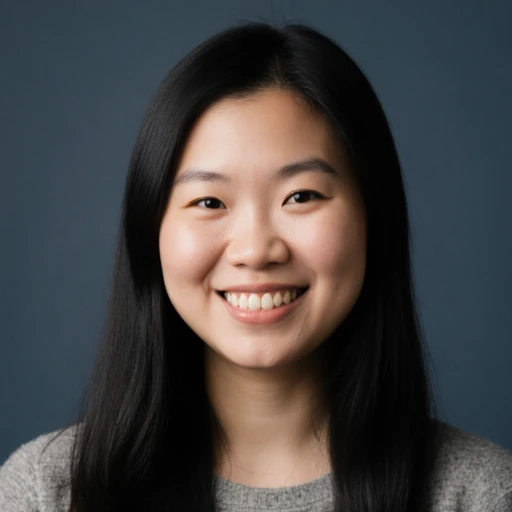
One of the most common methods for calculating forex risk involves understanding pip value and utilizing stop-loss orders. This approach allows you to define your maximum potential loss for each trade based on the distance between your entry point and your stop-loss level. It’s a simple yet powerful way to stay in control.
Step-by-Step Guide to Pip Value and Stop-Loss Risk Calculation
- Determine Your Stop-Loss Level: Based on your technical analysis, identify a price level where you’d want to exit the trade if it moves against you.
- Calculate the Distance in Pips: Subtract your stop-loss price from your entry price (or vice versa, depending on whether you’re buying or selling). The result is the number of pips at risk.
- Determine the Pip Value: The pip value varies depending on the currency pair and your account currency. Your broker should provide this information.
- Calculate the Total Risk: Multiply the number of pips at risk by the pip value and your position size. This will give you the total amount of money you stand to lose if your stop-loss is triggered.
For example, let’s say you’re trading EUR/USD, your pip value is $10, your stop-loss is 50 pips away, and your position size is 1 lot. Your total risk would be 50 pips * $10/pip * 1 lot = $500.
Important Note: Always factor in the potential for slippage, which can cause your stop-loss to be executed at a worse price than you intended.
Managing Risk with Position Sizing in Forex Trading
Position sizing is arguably the most critical aspect of forex risk management. It determines how much of your capital you allocate to each trade. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any single trade. Why so conservative? Because even the best traders experience losing streaks. Proper position sizing helps you weather those storms without blowing up your account.
Calculating Position Size Based on Risk Tolerance
Here’s how to calculate your ideal position size:
- Determine Your Account Balance: Know exactly how much capital you have available for trading.
- Set Your Risk Percentage: Decide what percentage of your account you’re willing to risk per trade (e.g., 1%).
- Calculate Your Risk Amount: Multiply your account balance by your risk percentage. This is the maximum dollar amount you’re willing to lose on a single trade.
- Calculate Your Position Size: Divide your risk amount by the total risk calculated in pips (as described in the previous section). This will give you the appropriate position size for your trade.
Let’s say you have a $10,000 account and you’re willing to risk 1% per trade. Your risk amount is $100. If your stop-loss is 50 pips away and your pip value is $10, your position size would be $100 / (50 pips * $10/pip) = 0.2 lots.
The Role of Leverage in Forex Risk Calculation
Leverage is a double-edged sword. It allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, potentially amplifying your profits. However, it also magnifies your losses. Using high leverage without proper risk management is a recipe for disaster. Are you truly prepared for the potential consequences?
Understanding the Impact of Leverage on Risk
The higher the leverage, the smaller the price movement needed to wipe out your trading account. For example, if you’re using 100:1 leverage, a 1% adverse price movement can result in a 100% loss of your invested capital. That’s why it’s crucial to use leverage responsibly and in conjunction with strict risk management techniques.
- Start with Low Leverage: If you’re new to forex trading, begin with low leverage (e.g., 10:1 or 20:1) and gradually increase it as you gain experience and confidence.
- Never Exceed Your Risk Tolerance: Even with leverage, always adhere to your predetermined risk percentage per trade.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders Diligently: Stop-loss orders are essential for limiting your losses when using leverage.
FAQ: Forex Risk Calculation
What is the most important factor in forex risk calculation?
Position sizing is arguably the most critical, as it directly controls the amount of capital at risk per trade.
How often should I review my risk management strategy?
You should review your risk management strategy regularly, especially after significant market events or changes in your trading style.
Is it possible to eliminate risk entirely in forex trading?
No, it’s not possible to eliminate risk entirely. However, you can significantly reduce it through proper risk management techniques.
What are some common mistakes traders make when calculating risk?
Common mistakes include using excessive leverage, neglecting stop-loss orders, and failing to account for slippage.